Operations are generally divided into two types-
- Restrictive – they decrease food intake (gastric banding, sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass)
- Malabsorptive – they decrease food absorption(Mini Gastric Bypass, Biliopancreatic diversion (BPD) or duodenal switch (DS)
Or a combination of both
All these surgeries are performed laparoscopically (with very small holes / cuts).
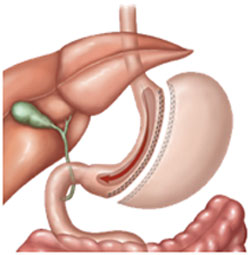
Sleeve Gastrectomy (SG)
This has become among the most common Bariatric Surgery world-wide. Sleeve Gastrectomy is designed to decrease appetite and produce the sensation of fullness with minimal oral intake. Ghrelin is a hungar causing hormone produced mainly by upper part of stomach (fundus) which is removed in this surgery.
Major advantages:
- It is more physiological as only stomach size is reduced and nothing is done to intestines.
- There is no foreign body, no anastomoses and no intestinal bypass.
- Chances of vitamin and micro-nutrient deficiencies are less.
- It can be easily converted to other procedures if required.
- May be safer in high risk individuals
Major dis-advantages:
- If patient tries to cheat sleeve by consuming large amount of high calorie liquid, patient can regain some of lost weight.
- Weight loss for very very obese patients may not be adequate but sleeve is considered first safer alternative in such patients as well.
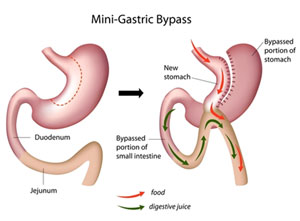
Mini-Gastric Bypass (MGB)
This is a mal-absorptive surgery which allows only a part of ingested food to be absorbed. Stomach is divided into two parts and patient can eat less as before. The new smaller stomach is attached to small intestine by bypassing first part of small intestine. The amount of bypass is calculated depending upon patient’s profile.
Major advantages
- Single anastomosis rather than 2 anastomosis of RYGB.
- More malabsorptive than restrictive as compared to RYGB, so patient can eat more food.
- May have better resolution of diabetes as compared to sleeve gastrectomy.
- Can be reversed or revised easily.
- Better suited for patients with hiatus hernia or severe acidity (reflux) as compared to sleeve gastrectomy.
- May give better results in super-obese as compared to sleeve gastrectomy.
Major disadvantages:
- It is more malabsoptive as compared to sleeve or RYGB, hence chances of vitamin, micro-nutrient and protein deficiency may be higher. Patient must commit for life-long suppliments.
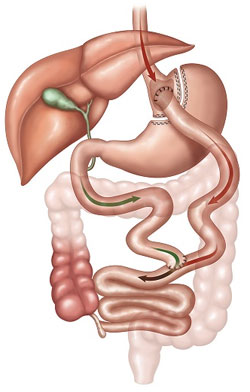
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB)
The Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) is the “gold standard” bariatric surgical procedure. RYGB is one of the most common bariatric procedure performed world-wide. The RYGB has both restrictive and malabsorptive properties due to the combination of a small stomach pouch and total bypass of the first part of small intestine.
Major advantages:
- May have better resolution of diabetes as compared to sleeve gastrectomy.
- Better suited for patients with hiatus hernia or severe acidity (reflux) as compared to sleeve gastrectomy.
- May give better results in super-obese as compared to sleeve gastrectomy.
- Bile can not re-enter stomach pouch as in MGB.
Major Disadvantages:
- Involves two joints in intestines.
- Stomach pouch is quite small and so is capacity to eat (but is sufficient for patient).
- Chances of vitamin and micro-nutrient deficiencies may be more as compared to sleeve gastrectomy.