Various surgeries when done not only for obesity or when done in lean patients to control metabolic diseases like Diabetes Type2, high blood pressure (Hypertension), severe joint pains etc, they are referred to as Metabolic Surgeries.
Definitions of overweight (BMI >25) and obesity (BMI>30) are based derived from Western populations. Studies have shown that for a given BMI, Asians have higher percentage of body fat and tend to have higher risks of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. According to WHO recommendations, a BMI of 18.5–22kg/m2 is considered healthy for Asian populations.
International Diabetes Federation (IDF) position statement in 2011 March also concluded surgery should be considered as an alternative treatment option in Asian patients with a BMI between 27.5 and 32.5 kg⁄m2 when diabetes cannot be adequately controlled by an optimal medical regimen.
Metabolic Surgery Recognized as a Standard Treatment Option for Type 2 Diabetes –
A Special Issue of Diabetes Care Reports First-Ever Clinical Guidelines for When to Recommend or Consider Metabolic Surgery as Treatment for People with Diabetes.
Learn More About Diabetes
What is diabetes?
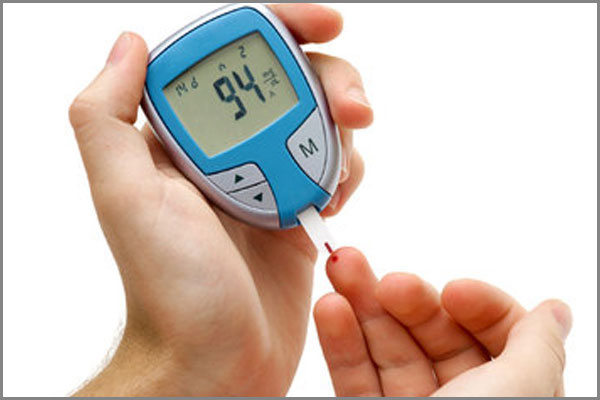
Diabetes is a condition where the amount of glucose in your blood is too high because the body cannot use it properly.
This is because your pancreas doesn’t produce any insulin, or not enough insulin, to help glucose enter your body’s cells – or the insulin that is produced does not work properly (known as insulin resistance).
- Insulin is the hormone produced by the pancreas that allows glucose to enter the body’s cells, where it is used as fuel for energy so we can work, play and generally live our lives. It is vital for life.
- Glucose comes from digesting carbohydrate and is also produced by the liver.
- If you have diabetes, your body cannot make proper use of this glucose so it builds up in the blood and can’t be used as fuel.
- There are two main types of diabetes: Type 1 diabetes and Type 2 diabetes.
What is insulin?
Insulin is a hormone. It works as a chemical messenger that helps your body use the glucose in your blood to give you energy. You can think of it as the key that unlocks the door to the body’s cells. Once the door is unlocked, glucose can enter the cells where it is used as fuel. In Type 1 diabetes the body is unable to produce any insulin so there is no key to unlock the door, and the glucose builds up in the blood.
- The body can't use glucose to provide energy and tries to get it from elsewhere and starts to break down stores of fat and protein instead. This can cause weight loss. Because the body doesn’t use the glucose it ends up passing into the urine.
- Nobody knows for sure why these insulin-producing cells have been destroyed, but the most likely cause is the body having an abnormal reaction to the cells. This may be triggered by a virus or other infection.
What is Type 1 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes develops when the insulin-producing cells in the body have been destroyed and the body is unable to produce any insulin.
Who typically gets Type 1 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes accounts for about 10 per cent of all adults with diabetes and is treated by daily insulin doses – taken either by injections or via an insulin pump. It is also recommended to follow a healthy diet and take regular physical activity. Type 1 diabetes can develop at any age but usually appears before the age of 40, and especially in childhood. It is the most common type of diabetes found in childhood.
What is Type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes develops when the insulin-producing cells in the body are unable to produce enough insulin, or when the insulin that is produced does not work properly (known as insulin resistance).
Who typically gets Type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes usually appears in people over the age of 40, though in South Asian people, who are at greater risk, it often appears from the age of 25. It is also increasingly becoming more common in children, adolescents and young people of all ethnicities. Type 2 diabetes accounts for between 85 and 95 per cent of all people with diabetes and is treated with a healthy diet and increased physical activity.
In addition to this, medication and/or insulin are often required.
In Type 2 diabetes there is not enough insulin (or the insulin isn’t working properly), so the cells are only partially unlocked and glucose builds up in the blood.